Intro
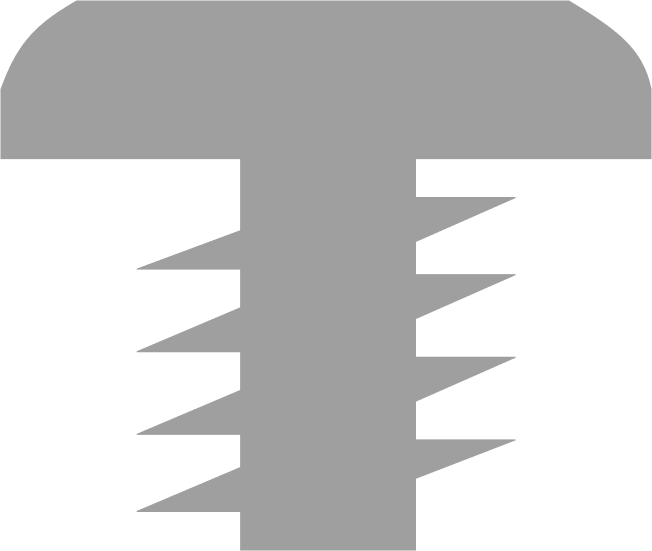
The head is a key component of the screw, providing two main functions; firstly, it is the stopping point for the screw once it has been driven into your chosen material, ensuring the fastener does not go deeper than it should. Secondly, the head is where the drive lives, or where the force is applied to drive in (or remove) the screw. In addition to these two main purposes, the head of the screw is also - generally speaking - the only part of the screw that is still visible once the job has been completed - due to this, consideration should be given to the aesthetics of the screw head type, if this is relevant for your project.
If you need help dissecting what different threads, heads and gauges do, take a look through our other Screw guide pages:
Screw Anatomy
Before we take a look at the different types of screws, it's a good idea to get acquainted with their different parts first:

Screw Head Types
For more specific information on a larger variety of different screw head types and what job each one is designed to tackle, take a look below:
Screw Drive Types
Despite there being so many different types of screw drives, they don’t really serve a different purpose and you can pretty much use any screw head in whatever application you have at hand. Some screw head types may be slightly better suited than others at times; slotted heads are a good choice for applications that require to be turned by hand, such as cabinetry and furniture-making. However, slotted head screws are largely incompatible with electric screwdrivers and, with so much power, the screwdriver will often slip out. Other heads are created to self-centre the screwdriver and make placing the screw a lot quicker and easier, such as the Pozidrive design.
Below are some screw head types, some of which you’re probably very familiar with and others have more niche and specific uses you may never have seen before.


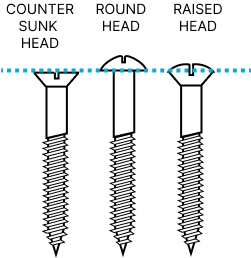
 Tip: The most common screw head size in timber construction is 5.0.
Tip: The most common screw head size in timber construction is 5.0.